dataset
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
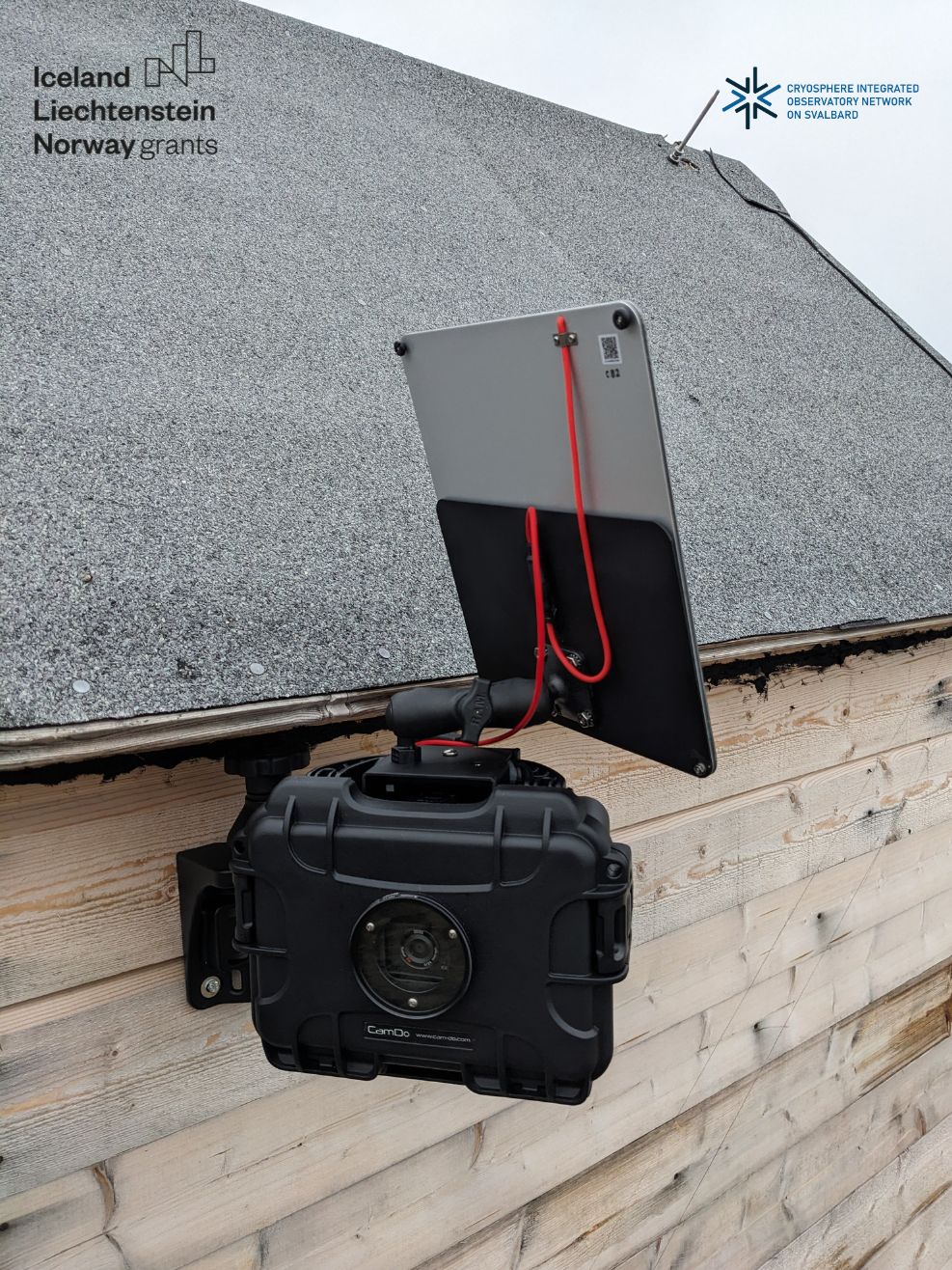

Time-lapse cameras In order to determine the state of coverage of the area, e.g. period of snow cover on a tundra, the extent of the glacier front, etc., it is necessary to perform photographic imaging at a specific time interval. This will allow for precise diagnosis of snow conditions. CRIOS – Cryosphere Integrated Observation Network on Svalbard Project financed from the EEA Financial Mechanism 2014-2021 operated by the National Science Centre in Poland Agreement no. UMO-2022/43/7/ST10/00001 to a predefined project no. 2022/43/7/ST10/00001 Project period: 08.09.2022 - 30.04.2024 (2029)
-
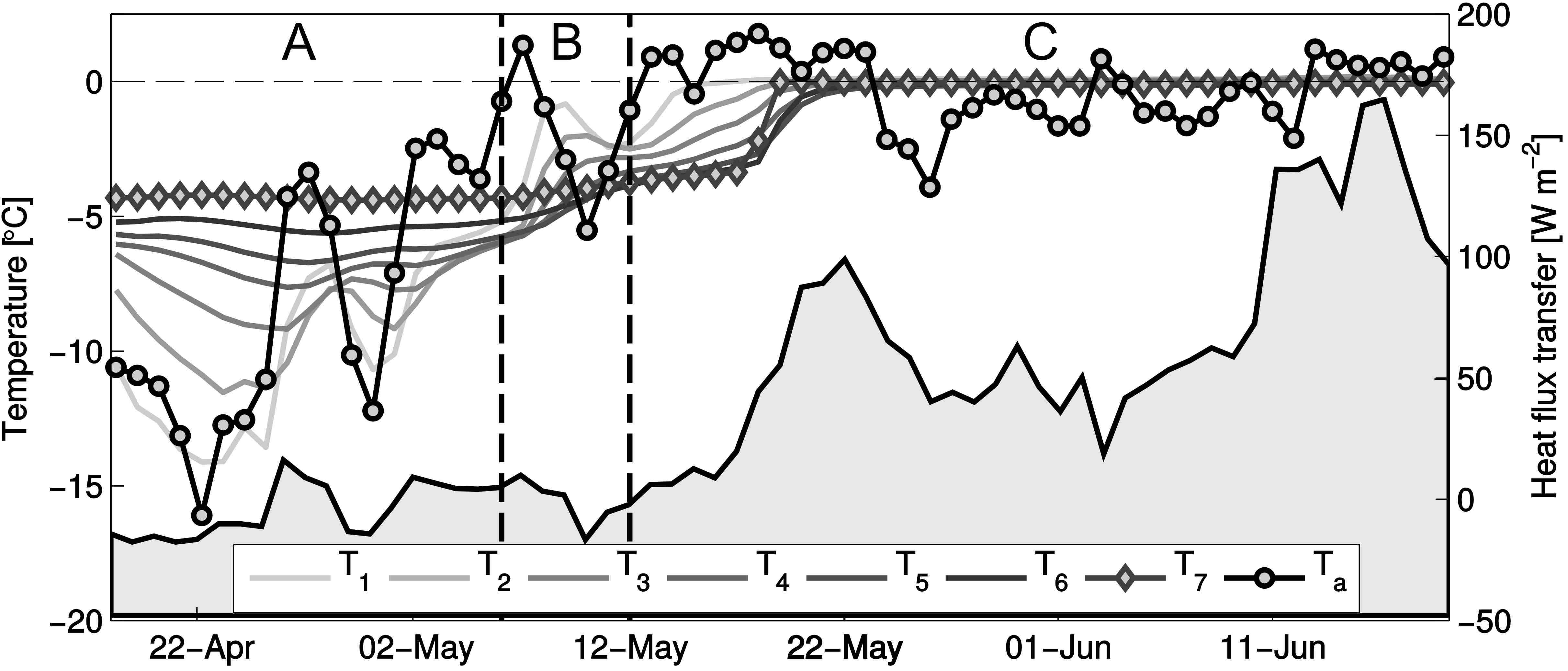
Dataset contains evolution of the snow temperature within seasonal snowpack on Hansbreen. Fieldwork has been performed with several thermistors located at different levels (from snow surface to the bottom, on glacier ice) from April to July 2010 (during period of early and intensive surface melting). Study has been repeated in 2015, at the same location. Acknowledgements: Research Council of Norway, Arctic Field Grant 2013: Spatial distribution of snow cover and drainage systems on the glaciers on Wedel Jarlsberg Land (RiS ID: 6158); the National Science Centre PRELUDIUM 4: Role of meltwater from snow cover for supplying drainage systems of the Spitsbergen glaciers (2012/07/N/ST10/03784) References: Laska M., Luks B., Budzik T., 2016. Influence of snowpack internal structure on snow metamorphism and melting intensity on Hansbreen, Svalbard. Polish Polar Research, 37(2): 193–218. doi:10.1515/popore-2016-0012
-

Time-lapse cameras In order to determine the state of coverage of the area, e.g. period of snow cover on a tundra, the extent of the glacier front, etc., it is necessary to perform photographic imaging at a specific time interval. This will allow for precise diagnosis of snow conditions. The camera is installed at the main entrance to the NCU Polar Station. The lens is pointed in a westerly direction, towards Prins Karls Forland CRIOS – Cryosphere Integrated Observation Network on Svalbard Project financed from the EEA Financial Mechanism 2014-2021 operated by the National Science Centre in Poland Agreement no. UMO-2022/43/7/ST10/00001 to a predefined project no. 2022/43/7/ST10/00001 Project period: 08.09.2022 - 30.04.2024 (2029)
-
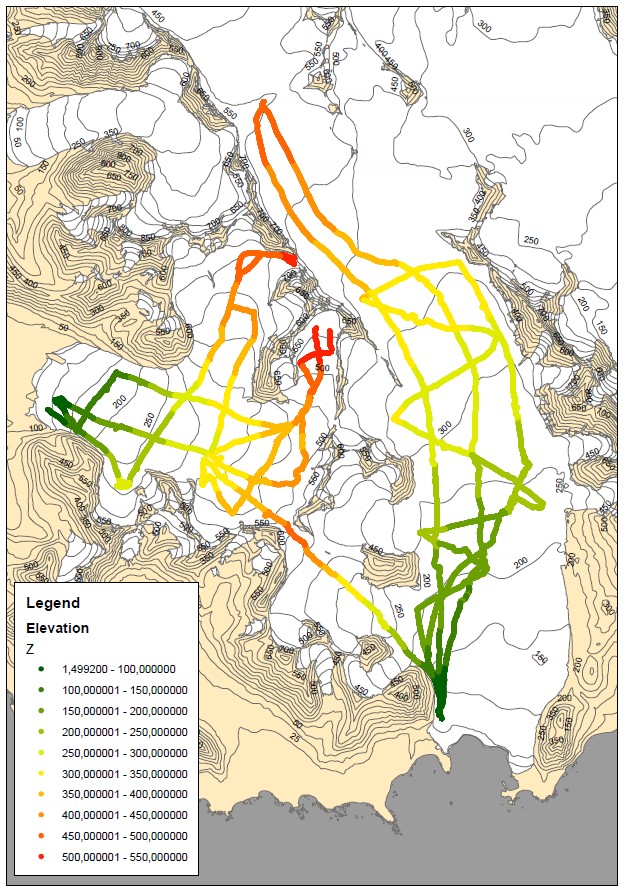
Dataset contains surface elevation along spring GPR profiles performed on Hansbreen and Werenskioldbreen. Fieldwork has been done with dGPS device in kinematic mode at the end of ablation season in 2013 and 2015 to compare it with spring GPR survey and calculate surface ablation. Acknowledgements: Research Council of Norway, Arctic Field Grant 2013: Spatial distribution of snow cover and drainage systems on the glaciers on Wedel Jarlsberg Land (RiS ID: 6158); the National Science Centre PRELUDIUM 4: Role of meltwater from snow cover for supplying drainage systems of the Spitsbergen glaciers (2012/07/N/ST10/03784)
-
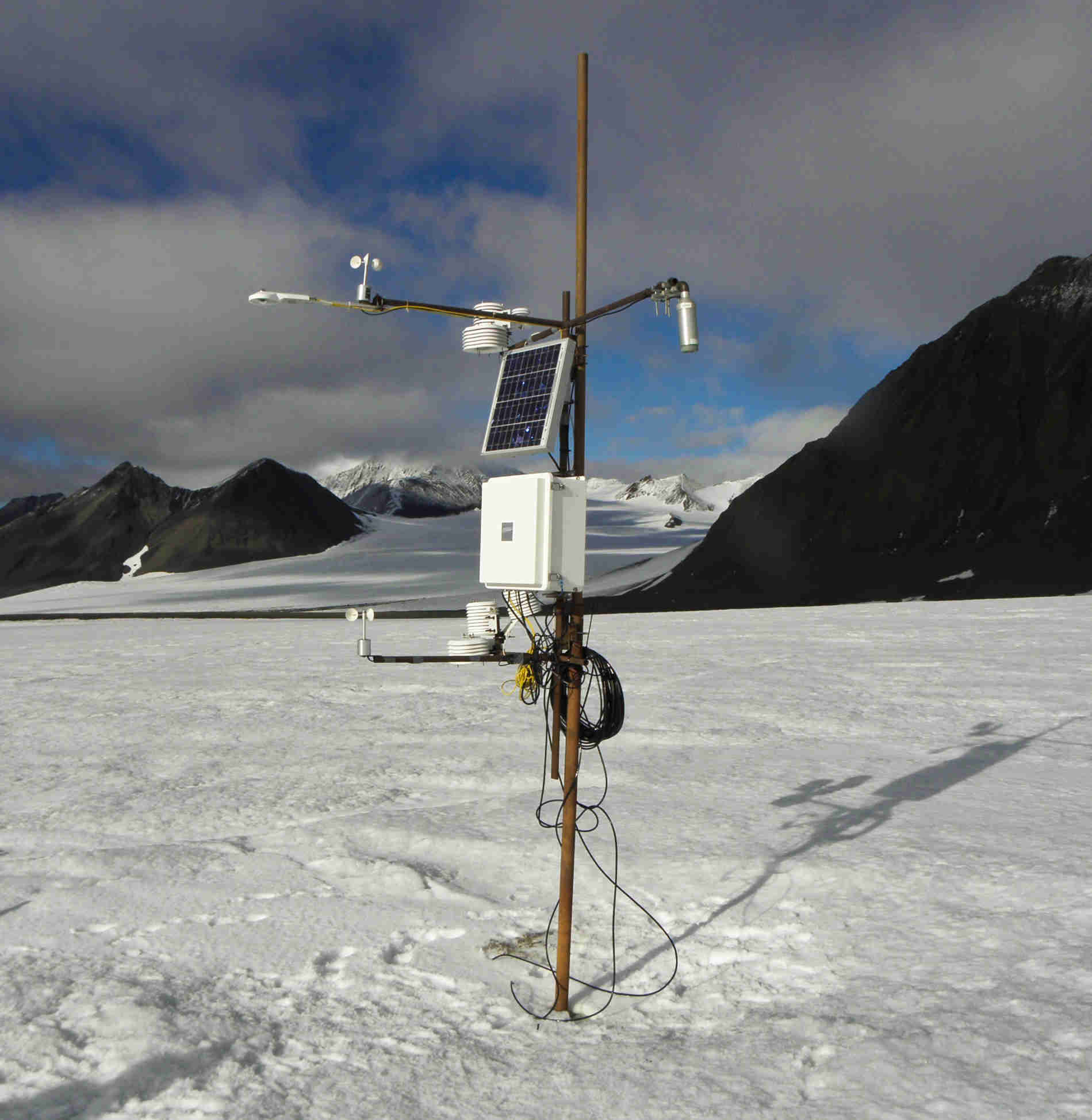

Upwelling shortwave flux in air measurements from AWS located on the Werenskioldbreen. The sensors are installed on a mast that is mounted in the glacier ice. During the season, the distance between the glacier's surface and the sensors increases. The station is serviced at least once a year between March and April.
-
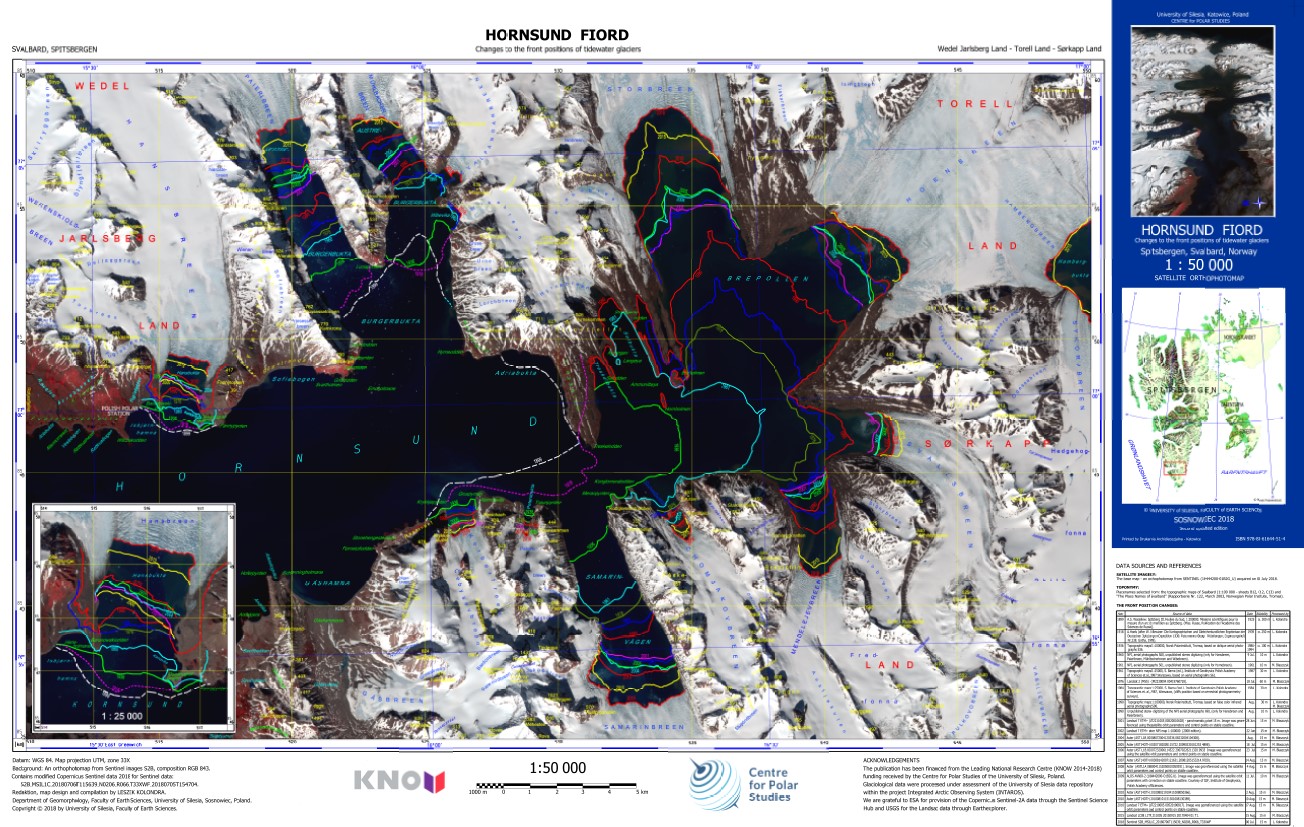
The ortophotomap of Hornsund Fiord with changes to the front positions of tidewater glaciers. The front positions are based on different cartographical maps and satellite data. The base map is Sentinel 2 satellite image acquired on 6 July 2018. Citation: Kolondra L., 2018. Hornsund Fiord - Changes to the front positions of tidewater glaciers. University of Silesia, Faculty of Earth Sciences.
-

Time-lapse cameras In order to determine the state of coverage of the area, e.g. period of snow cover on a tundra, the extent of the glacier front, etc., it is necessary to perform photographic imaging at a specific time interval. This will allow for precise diagnosis of snow conditions. The camera is installed in the glacier catchment area at the hydrological station. CRIOS – Cryosphere Integrated Observation Network on Svalbard Project financed from the EEA Financial Mechanism 2014-2021 operated by the National Science Centre in Poland Agreement no. UMO-2022/43/7/ST10/00001 to a predefined project no. 2022/43/7/ST10/00001 Project period: 08.09.2022 - 30.04.2024 (2029)
-
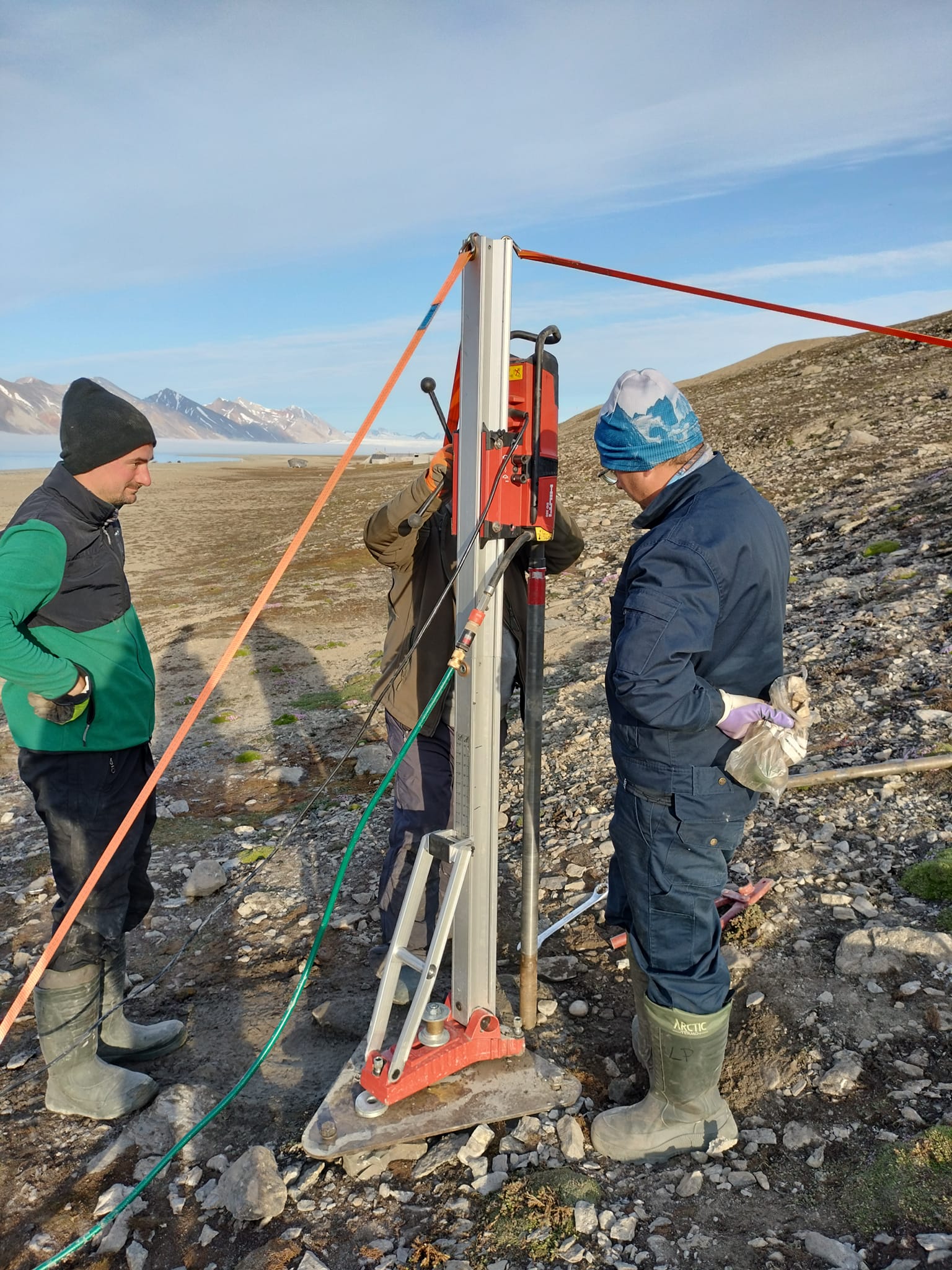

Permafrost monitoring System of thermistors (temperature strings with loggers) to monitor the ground thermal state Precise data on the thermal state of the frozen ground is one of the key missing components of the environmental monitoring at the research stations spread across Spitsbergen. The CRIOS project will allow us to equip the newly established borehole with precise temperature strings that will record ground thermal changes over the next couple of years. A system of temperature strings will be used in the monitoring of the thermal state of permafrost in drilled boreholes. Devices were tested in severe weather and are commonly used for permafrost monitoring by other research groups working in polar regions. Site Information The borehole near the UMK station in Kaffioyra was located at the existing meteorological garden, about 100 m from the shoreline. The drilling was carried out on 20-21.07.2023. The substrate is dominated by loose sandy-gravel beach sediments. A large amount of fine material and the formation of a core in a small part of the hole made it possible to reach a depth of 10.0 m below sea level. CRIOS – Cryosphere Integrated Observation Network on Svalbard Project financed from the EEA Financial Mechanism 2014-2021 operated by the National Science Centre in Poland Agreement no. UMO-2022/43/7/ST10/00001 to a predefined project no. 2022/43/7/ST10/00001 Project period: 08.09.2022 - 30.04.2024 (2029)
-
Glaciers facies extents of Langjökull delivered from unsupervised classifications of fully-polarimetric SAR data (ALOS-2 PALSAR, RADARSAT-2) for 2018 year. Date of SAR images acquisitions: 12, 16 Mar 2018 (Fine Quad Pol RADARSAT-2), 17 Mar 2018 (High Sensitive Quad Pol ALOS-2 PALSAR). Method of classification: H-a Wishart Classification. Results validated with terrestrial measurements (shallow ice cores drilling, Ground Penetrating Radar measurements). Research done with cooperation with University of Iceland and supported by the European Space Agency, Third Party Miassions. Overwiew of results of RADATSAT-2 (16 Mar 2018; Fine Quad Pol) classification of south part of Langjökull. Black line - contour of Langjökull; other colours - different scattering properties of SAR microwaves. For more details please contact Barbara Barzycka (bbarzycka@us.edu.pl).
-
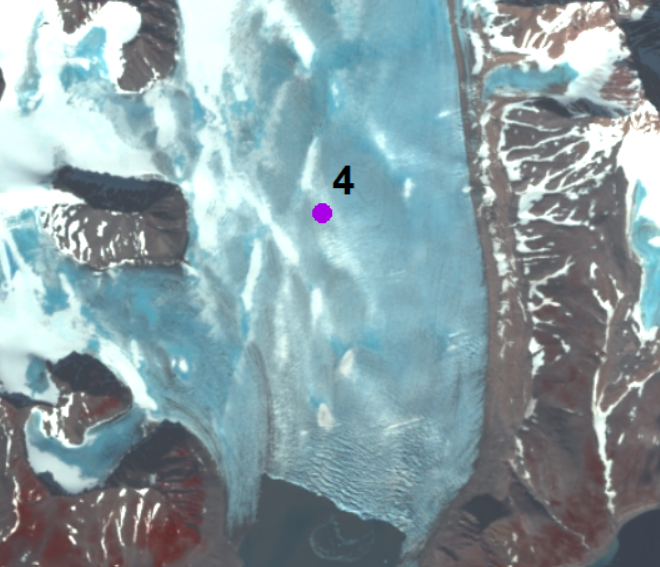
The annual velocity of Hansbreen in the period 2007–2015 is determined at stake No. 4 located approximately 3.5 km upstream of the glacier terminus (15°28`E, 77°02`N). Monitoring of the glacier is conducted by Institute of Geophysics Polish Academy of Science. The stake position was measured by the differential GPS receiver at the turn of each year (December/January) (with a horizontal accuracy of ±4 cm). Velocity along the Hansbreen terminus in 2009 and 2015 is processed from repeated terrestrial laser scanning in August 2009 and August 2015. Values of displacements of the same features along the calving front (distinctive edges of crevasses) for approximately two weeks were provided with an accuracy of around 10 cm. The database is the supplement to the paper: Małgorzata Błaszczyk, Jacek A. Jania, Michał Ciepły, Mariusz Grabiec, Dariusz Ignatiuk, Leszek Kolondra, Aleksandra Kruss, Bartłomiej Luks, Mateusz Moskalik, Tadeusz Pastusiak, Agnieszka Strzelewicz, Waldemar Walczowski, Tomasz Wawrzyniak. “Factors controlling terminus position of Hansbreen, a tidewater glacier in Svalbard”, Journal of Geophysical Research - Earth Surface, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JF005763.
 Centre for Polar Studies
Centre for Polar Studies