cold ice, temperate ice, thermal regime, GPR, RES
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
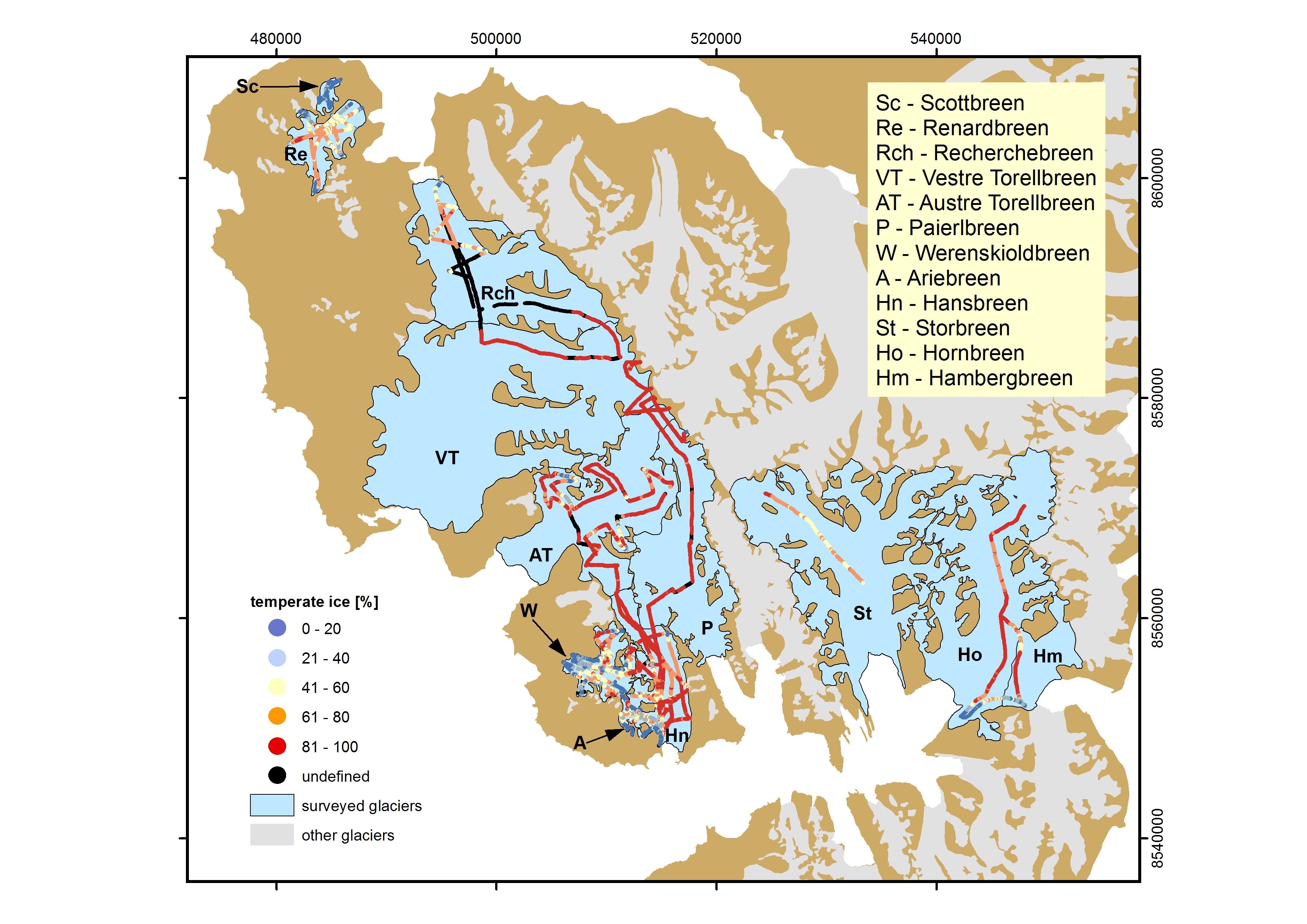
Thermal structure of selected S Spitsbergen glaciers was derived from ground based radio-echo sounding (RES). The division between cold and temperate ice layers is based on indirect interpretation of GPR (ground penetrating radar) image. Cold ice layer is virtually “transparent” for radio waves, while temperate ice layer is characterised by numerous diffractions on water inclusions. The database contains results from 479.7 km of RES profiles acquired in 2007-2014 on 12 glaciers in Wedel Jarlsberg Land and Torell Land (S Spitsbergen) including: Amundsenisen, Austre Torellbreen, Vestre Torellbreen, Hansbreen, Storbreen, Hornbreen, Hambergbreen, Recherchebreen, Scottbreen, Renardbreen, Werenskioldbreen and Ariebreen. Basic characteristics of investigated glaciers and its thermal structure is provided in table 1 (supplementary information). The surveys used GPR antennas in range 25-200 MHz, selected according to expected ice depth. Thanks to that on 87% of the profiles ice/bed interface has been identified. The radar system was pulled behind the snowmobile moving with velocity c. 20 km h-1. Applying trace interval 0.2-1.0 s, trace-to-trace distance was in range 1-5m. Trace positions were acquired by GNSS receivers working in navigation or differential mode with respective accuracy 3.0 m and 0.1m. RES data were processed applying standard filtering procedure (DC-offset, time-zero adjustment, 2-D filter, amplitude correction and bandpass filtering). Time-to-depth conversion used average radio wave velocity (RWV) for glacier ice 16.4 cm ns-1, 16.7 and 16.1 for cold and temperate ice respectively, based on CMP survey. More precise description of data collection, processing and quality is provided by Grabiec (2017). In S Spitsbergen polythermal glaciers are predominant. 57.8% of surveyed profiles consist of both: temperate and cold ice layers; 22.7% profiles is entirely temperate while 6.6% contains cold ice only (remaining profiles have undefined thermal structure). Studied glaciers represent broad spectrum of polythermal structure with cold-to-temperate ice ratio from 99:1% (Ariebreen) to 2:98% (accumulation zone of Vestre Torellbreen). The data were collected and processed under following projects: • IPY/269/2006 GLACIODYN The dynamic response of Arctic glaciers to global warming • UE FP7-ENV-2008-1 ice2sea Estimating the future contribution of continental ice to sea-level rise • PNRF-22-AI-1/07 AWAKE Arctic Climate and Environment of the Nordic Seas and the Svalbard – Greenland Area • NCBiR/PolarCLIMATE-2009/2-1/2010 SvalGlac Sensitivity of Svalbard glaciers to climate change • Pol-Nor/198675/17/2013 AWAKE-2 Arctic climate system study of ocean, sea ice and glaciers interactions in Svalbard area • 03/KNOW2/2014 KNOW Leading National Research Centre Reference: Grabiec M. 2017: Stan i współczesne zmiany systemów lodowcowych południowego Spitsbergenu w świetle badań metodami radarowymi. Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Śląskiego, 328 s.
 Centre for Polar Studies
Centre for Polar Studies